The decision was formalized at a regional meeting on responding to mpox and other health emergencies, held in Nairobi, the capital of Kenya, according to a press release from the Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC).
At the meeting, representatives from Angola, São Tomé and Príncipe, Democratic Republic of Congo (DRCongo), Burundi, Malawi, Rwanda, Uganda, South Sudan, Zambia, Kenya, People's Republic of Congo and Central African Republic committed to cooperating with international organizations, civil society and health experts from across the continent to facilitate a response to the prevention and control of disease outbreaks, the entity explained.
"Epidemics know no borders, hence the need to strengthen cross-border collaboration and coordination," said Linda Mobula, World Bank health specialist in the DR Congo.
The agreement also aims to improve challenges related to cross-border transmission, data sharing mechanisms between countries and monitoring the mobility of affected populations, the Africa CDC said.
"It is also expected that this commitment will boost financial and technical resources for sustainable strategies to respond to mpox," he said.
The World Bank, in collaboration with the African Union's public health agency, the World Health Organization (WHO) and other partners such as UNICEF (United Nations Children's Fund) and the International Organization for Migration (IOM), convened the meeting to foster political engagement, technical discussions and cooperation among countries and stakeholders.
“The regional dimension of the mpox outbreak demands a collective solution. That is why this meeting is so important — it is not only a forum for knowledge exchange, but also a platform for joint action,” said mpox, Acting Regional Manager for Emergency Response at the WHO Regional Office for Africa.
The response to mpox is based on pillars such as epidemiological surveillance, laboratory diagnosis, clinical management, vaccination, research, risk communication, sustainable financing, policy alignment and capacity strengthening, which were discussed throughout the meeting, said the Africa CDC.
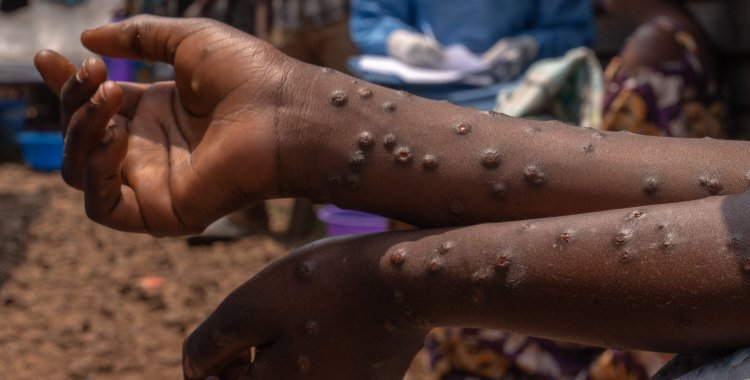
Africa has recorded a total of 132,954 cases (30,668 confirmed by analysis) and 1,761 deaths (176 confirmed by tests) due to Mpox infection since the beginning of 2024, the Africa CDC revealed on May 15.
The DR Congo, Angola's neighboring country, continues to be the epicenter of the disease, with 101,460 cases (18,354 confirmed) and 1,761 deaths (107 confirmed) since the beginning of 2024, concentrated in the east of the country, which has constantly faced episodes of violence since 1980.